Publications
Reviewer for T-ITS, NIPS 2025, AAAI 2026, ICLR 2026
2026
-
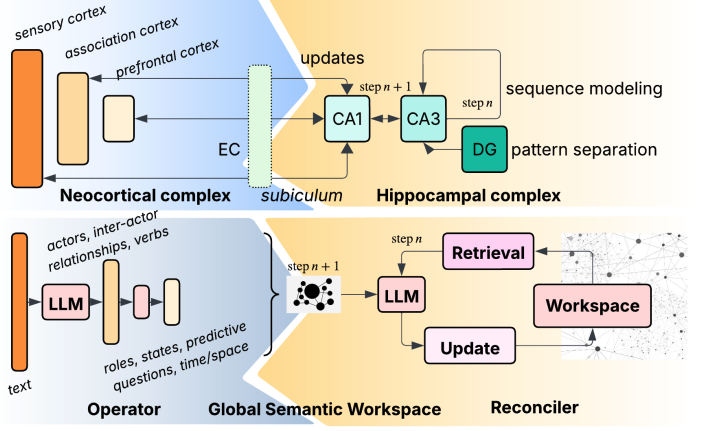 AAAI 2026 Oral Beyond Fact Retrieval: Episodic Memory for RAG with Generative Semantic WorkspacesIn International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) 2026
AAAI 2026 Oral Beyond Fact Retrieval: Episodic Memory for RAG with Generative Semantic WorkspacesIn International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) 2026
Reviewer for T-ITS, NIPS 2025, AAAI 2026, ICLR 2026
 AAAI 2026 Oral
AAAI 2026 Oral